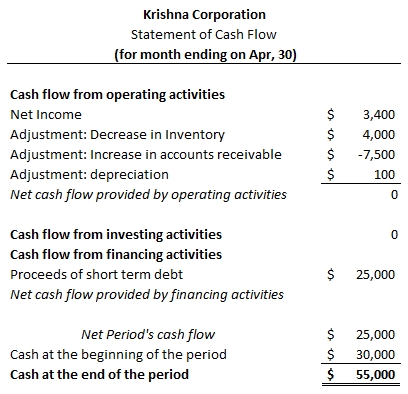
STATEMENT OF CASHFLOW
This is the third financial statement that John needs to understand in order to track his business efficiently. Cash flow statement will help John understand, how cash values have changed in the accounts of Supreme Car rental over the reported period. Using this statement, John can track & control cash generated and used by his company’s operating, investing and financing activities.
SUMMARY
Our entire discussion on introduction to accounting can be summarized using following points –
When a company pays cash for something, the company will credit Cash and will have to debit a second account. Assuming that a company prepares monthly financial statements—
- If the amount is used up or will expire in the current month, the account to be debited will be an expense account. (Advertising Expense, Rent Expense, Wages Expense are three examples.)
- If the amount is not used up or does not expire in the current month, the account to be debited will be an asset account. (Examples are Prepaid Insurance, Supplies, Prepaid Rent, Prepaid Advertising, Prepaid Association Dues, Land, Buildings, and Equipment.)
- If the amount reduces a company’s obligations, the account to be debited will be a liability account. (Examples include Accounts Payable, Notes Payable, Wages Payable, and Interest Payable.)
When a company receives cash, the company will debit Cash and will have to credit another account. Assuming that a company will prepare monthly financial statements—
- If the amount received is from a cash sale, or for a service that has just been performed but has not yet been recorded, the account to be credited is a revenue account such as Service Revenues or Fees Earned.
- If the amount received is an advance payment for a service that has not yet been performed or earned, the account to be credited is Unearned Revenue.
- If the amount received is a payment from a customer for a sale or service delivered earlier and has already been recorded as revenue, the account to be credited is Accounts Receivable.
- If the amount received is the proceeds from the company signing a promissory note, the account to be credited is Notes Payable.
- If the amount received is an investment of additional money by the owner of the corporation, a stockholders’ equity account such as Common Stock is credited.
Under accrual accounting basis, revenues from sales/service are to be recorded when the service or sale has been performed and not when the cash is received. This reflects the basic accounting principle known as the revenue recognition principle.
Expenses which can be co-related with revenues are to be booked in the period same as that of its matching revenue. Expenses which cannot be co-related to revenues are to be booked in the period in which they are incurred (and not in the period when the they were paid). This reflects the basic accounting principle known as the matching principle.
Table of Contents : Accounting Principles
Accounting Principles & guidelines