ACCRUAL V/S CASH BASIS OF ACCOUNTING
There are two methods of bookkeeping –
- Accrual basis of accounting &
- Cash basis of accounting
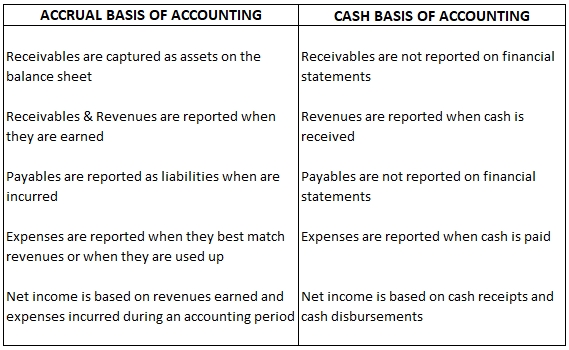
Accrual basis of accounting is based on the Revenue recognition principle and the Matching principle. Under this accounting technique :
- Revenue is said to be earned in the period in which the service is provided or the product is delivered by the company. It may or may not necessarily be the same period in which the company receives money for it
Example. A retailer sold & delivered merchandise to his customer with an agreed 30 days payment period in the last week of Aug, 2020. Under accrual accounting basis, Retailer is required to consider & report this transaction under sales revenue while generating monthly Income statement for Aug 2020. The fact that he is likely to receive payment for this sale only in the month of Sep, 2020 is irrelevant under this bookkeeping technique.
- Expenses that have cause & effect linkage with the revenues are to be reported along with it, in the same accounting period in which the revenue was earned (and not in the period in which they were incurred or paid off)
Example. Cost of goods sold (COGS), Sales commission etc can be linked to revenues and thus must be reported in period where the related revenue is earned and not in periods where these costs were actually incurred or paid off.
- Expenses that do not have any direct relationship with the revenues are to be reported in the accounting period in which they are incurred
Example. Utilities expense, Wages expense, Advertising expense, Depreciation expense, Research & development expense, Income tax expense etc are to be reported on profit & loss statement in the period in which they are incurred.
Some business scenarios might require prepayments from customers in order to process their sales or service orders. Under accrual accounting basis, these prepayments cannot be reported as revenue for the organization as they are not yet earned. Customer deposits or prepayments are to be reported as liability under Deferred Revenue head until the products or services are delivered.
On balance sheet, following intermediate holdings accounts can be tracked when accrual basis of accounting is used –
- Prepaid Expenses (e.g. prepaid insurance)
- Accounts Payable
- Accounts Receivables
- Interest Receivables
- Deferred Revenues ( or, Unearned revenue)
Alternatively, under the cash accounting basis, revenue or sales is recorded only when the cash is received. Similarly, expenses are reported in periods only when they are paid off.
Both the bookkeeping techniques can be summarized as below –