FRAMEWORK
A business can use a variety of pricing strategies when selling a product or service. Pricing strategies determine the price companies set for their products. The price can be set to maximize profitability for each unit sold or from the market overall. It can also be used to defend an existing market from new entrant, to increase market share within a market or to enter a new market. Pricing strategies can bring both competitive advantages and disadvantages to its firm and often dictate the success or failure of a business: thus it is crucial to choose the right strategy.
Typical pricing scenarios that candidates can witness in case based interviews are :
#1: Pricing of New Product(s)/ Service(s)
Sample Question: Our client has developed a new 200 watts mobile charger that can charge any supported device from 0-100% in less than 30 mins. How are we going to price it? What’s our strategy and why?
#2: Price Optimization of Existing Product(s)
Sample Question: Our client, a smartphone manufacturer is witnessing an increase in year-on-year sales volume, but their revenues has remained flat.
A typical pricing strategy takes into account segments, ability to pay, market conditions, competitor actions, trade margins and input costs, amongst others. It is targeted at the defined customers and against competitors.
Below section discusses the recommended thought process that one can use for structuring such business scenarios.
IDENTIFY THE OBJECTIVE
Adoption of an appropriate pricing strategy by a company is highly dependent on what it is aiming to achieve. A company focusing on profitability might charge premium from its customers whereas another one expecting to increase its market share might wish to go for a competitive pricing.
A company wishing to focus on both the objectives need to perform an in-depth analysis of its product/service. In case, the product is patented or has a specific usage, a premium can be charged on it. On the other hand, products which are generic in nature are to be sold competitively in the market.
Objectives affecting Pricing Strategy:
- Increase market share
- Increase profitability
- Defend existing market from new entrant
- Enter a new market/ New product launch
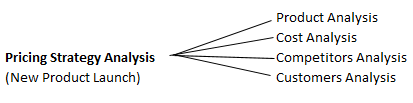
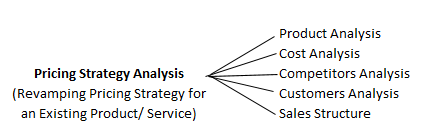
Depending on the case objective, one of more of the following analyses would be required to identify the apt pricing strategy for the client –
Pricing Strategy Framework
1. Product Analysis
- Product differentiation: Features & Qualities (What’s special or proprietary about our products?)
- Identify product substitutes.
- Is our product/ technology patented?
- Identify other advantages/ disadvantages linked with the product?
- What are our R&D Costs (if any)?
2. Cost Analysis
- Analyze product’s cost structure (major cost heads , cost metrics etc)
- How strong is client’s suppliers network? Whether raw material is procured at competitive or premium pricing?
- How are our switching costs from one supplier to another for major ingredients?
- In case client is part of a bigger value chain, identify the switching costs of our customer from us to other vendor
3. Competitors Analysis
- How are competitors performing relative to us? How are they pricing similar & substitute products?
- How are competitor’s market share?
- How is the supply & demand of similar products in the market?
4. Customer's Analysis
- Identify customer segmentation, market trends and customer’s willingness to pay (WTP) for the product?
- Evaluate Consumer buying habits?
- Do we need to spend the money to educate the customers?
5. Sales Structure
- Does the client offers bulk purchases discount to its customers?
- If yes, what discounting levels & policies are in practice right now?
- How has client structured sales incentives for its workforce?
- Is client following volume based incentive structure or profit based incentive structure?
Depending on the output of the above analysis, one of the below pricing strategies can be explored & adopted.
Pricing Strategies
- Competitive Pricing
- Product is to be priced competitively in the market i.e. slightly undercutting the competition in the segment
- Recommended if the product is generic or the company is aiming to capture market share
- Cost based Pricing
- Identify Cost of goods sold (COGS) for the product/ service being offered; Add on a fixed margin on its top to derive the price for the offering
- Recommended if the product is generic and there is little information available about the market & its players
- Price Based Costing
- Product is to be priced as per customer’s willingness to pay (WTP) for the offered product/service
- Recommended for niche/ patented products or when demand for a product/service is a lot more than its supply
It is important to understand that not all the analyses discussed above will make sense in a particular business scenario. The framework presented above is only to help candidate in structuring his thoughts in a more presentable way.