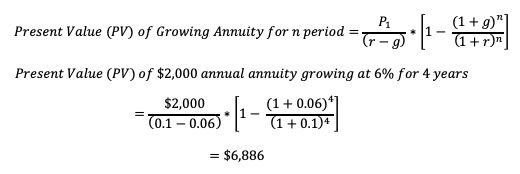ANNUITY
An annuity is a series of payments made at equal intervals for a defined period of time. Examples of annuities are monthly repayment of home loans/ mortgages, regular deposits to a savings account, payment of insurance premium and pension payouts.
1. PRESENT VALUE (PV) OF ANNUITY
Present value (PV) of an annuity for n periods can be calculated using the below formula:
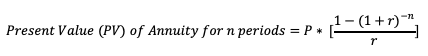
Where, P = Periodic Payment, r = discount rate, n = Number of periods
Above formula determines the present value for a series of future periodic payments made at a given time. The formula shown above is applicable to only ordinary annuity under following assumptions that:
- The periodic payment amount & the discount rate does not change
2. PRESENT VALUE (PV) OF ANNUITY: DERIVATION
The present value for a series of payments, whether they are the same or not, is calculated using the below formula:
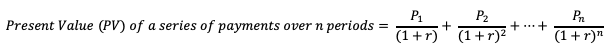
When the payments/dividends for each period are all the same, this equation turns into a geometric series. Using the sum formula for geometric progression, above equation can be re-written as:
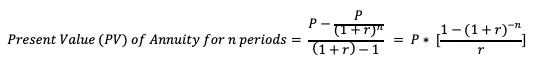
Example.Calculate the present value for annuity payment of $2000 per year for 4 years; discounted at 10% rate.
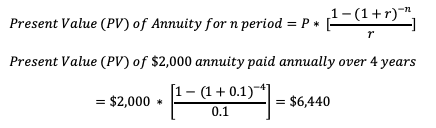
3. PRESENT VALUE (PV) OF A GROWING ANNUITY
The Present value of a growing annuity indicates the present-day value of a series of future periodic payments that are growing at a proportionate rate. A growing annuity is also termed as an increasing annuity.
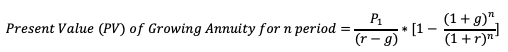
Where, P1 = First Payment, r = rate per period, g = growth rate, n = number of periods
4. PRESENT VALUE (PV) OF A GROWING ANNUITY: DERIVATION
The present value of a growing annuity is the sum of future cash flows that is increasing at a certain rate. It can be calculated as follows:
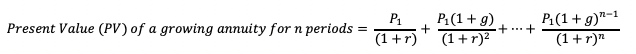
Above equation can be considered as a geometric progression with (1+g)/(1+r) as the common ratio. By using the sum formula for geometric series, the present value of a growing annuity can be re-written as:
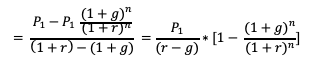
Example. Calculate the present value for the annual annuity payment of $2,000 growing at 6% rate per year for 4 years; consider discount rate = 10%