INTRODUCTION TO ADJUSTING ENTRIES
Adjusting entries are the additional journal entries made in the system to improve the accuracy of the financial statements. These entries are recorded in the system at the period-end just before publishing the financial statements. Adjustment entries are made to handle primarily two business scenarios –
- Capture the impact of those expenses and revenues heads which did occur but against which no entries are yet recorded in the books (Accrual scenarios)
- Some revenue or expense head has already been recorded in the books, but the amount needs to be divided across the current & future accounting periods. (Deferral scenarios)
To understand the concept of adjusting entries, consider the following scenarios:
Scenario 1. A company borrowed money from a bank on April 1, 2021 with an agreement that the interest payment on this loan would happen every quarter. As per the agreement, the first interest payment against this loan will be due on June 30, 2021.
Considering the company has monthly period closure policy, the accounting records generated at the month-end of April will not contain any payment entry to the bank for the interest incurred from April 1 to April 30 duration (since no interest payment was made in the period), although in reality this loan is costing the company an interest expense for each day. Thus, the Income statement derived in such scenarios will never report profitability precisely because of these missing interest entries in the period. This is where the concept of adjusting entries comes to rescue.
For the company to report its income statement precisely for any period, it should also report its liabilities arising from such business scenarios in the form of additional journal entries called adjusting entries. In our case, below journal entry/ adjusting entry would be additionally required in the system to ensure the completeness of Income statement for the reported period.
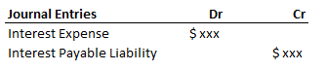
Scenario 2: Another scenario, where adjusting entries comes to rescue is when some revenue or expense head has already been recorded in the books, but the amount needs to be divided across the current & the future accounting periods. Purchase of insurance by a company is one such item that falls in this category. Say a company purchased an insurance for a period of 1 year on 1st January, 2021 and paid an upfront premium of $3600 for it. Here although the insurance is valid for next 12 months, still all of its cost i.e. $3600 was paid in the first month itself.
If the company were to report Income statement for January period (without any adjusting entry), it will consider all of the $3600 amount as insurance expense for the period and thus will report an undervalued profitability. However, in reality only $300 ($3600/12) has to be reported as insurance expense for January period. This is again taken care by recording additional journal entries/ adjusting entries as below:
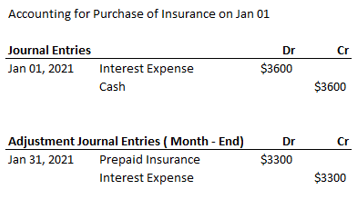
$3300 will be reported as an asset (Prepaid insurance) here on company’s balance sheet at the month end of January, 2021.
TYPES OF ADJUSTING ENTRIES
Adjusting entries can be grouped into following categories –
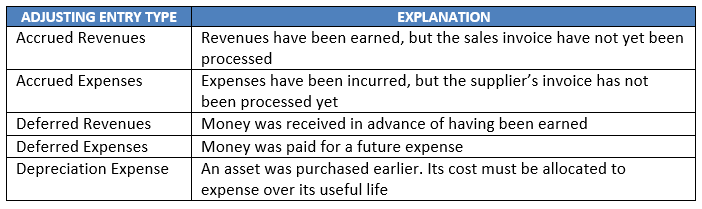
Table of Contents : Accounting Principles
Accounting Principles & guidelines