INCOME STATEMENT FORMATS
There are multiple formats of income statements which are used by different organizations for reporting. Income statements are often accompanied by statement of retained earnings. Following section discusses each of these formats in detail –
1. SINGLE-STEP INCOME STATEMENT
A single step income statement captures broadly two major sections. It starts with capturing income heads resulting in cash inflows for the organization like sales revenues, gains, non-operating revenues etc; followed by second section which captures all the expense heads for the organization resulting in cash outflow like operating expenses, losses, non-operating expenses etc. Net income is therefore calculated using the following formula –
NET INCOME = (REVENUES + GAINS) - (EXPENSES + LOSSES)
A simplified version of a single step income statement would look like something below –
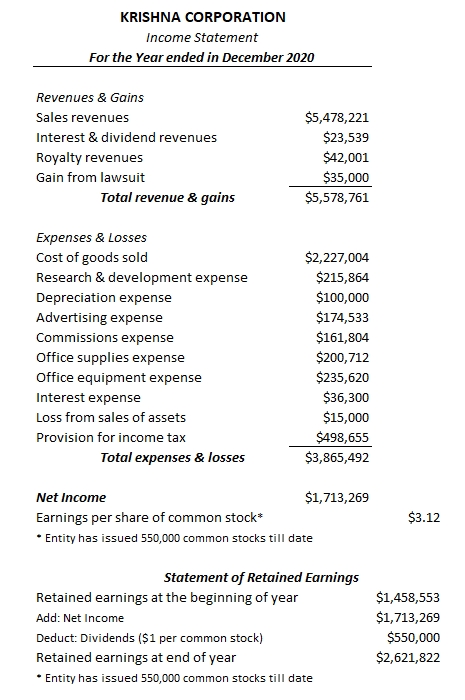
2. MULTI-STEP INCOME STATEMENT
The multi-step income statement captures operating revenues & expenses and non-operating revenues & expenses separately in different sections of the document. Thus it provides a lot more direct insights into the financial health of the organization than a single step income statement. Following definitions can be used to better understand multi-step income statements.
GROSS PROFIT = NET SALES REVENUE - COST OF GOODS SOLD
OPERATING INCOME = OPERATING REVENUE - OPERATING EXPENSES
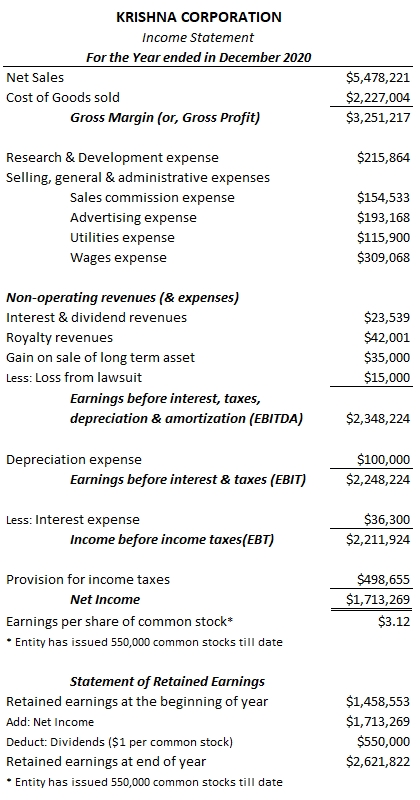
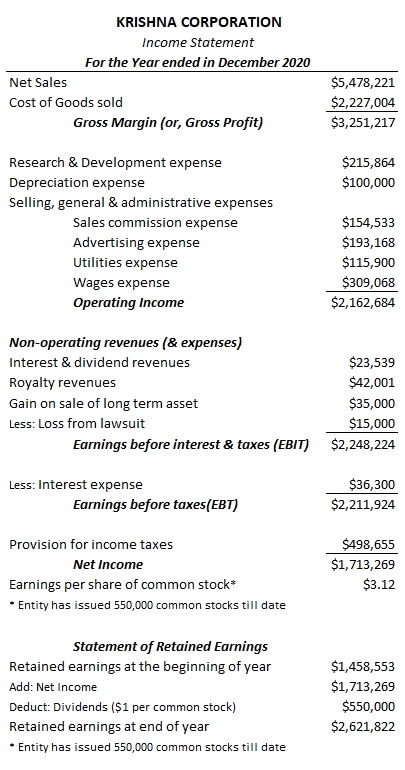
Two popular versions of multi-step Income statements are captured as below for KRISHNA CORPORATION. They are practically the same statement reported in two different formats. Format 1 focuses on reporting EBITDA metric while Format 2 focuses on reporting Operating income on the income statement.
EBITDA FORMAT: INCOME STATEMENT
OPERATING INCOME FORMAT: INCOME STATEMENT
EBITDA & Operating income, both of these metrics are equally useful for investors and can be calculated as below if not already present on the income statement.
OPERATING INCOME = EBIT - NON-OPERATING REVENUE + NON-OPERATING EXPENSES
EBITDA = NET INCOME + TAXES + DEPRECIATION & AMORTIZATION
Example. As an example, if someone decides to calculate operating income using EBITDA Format of Income statement, he may do using the below formula –
OPERATING INCOME = EBIT – NON-OPERATING REVENUE + NON-OPERATING EXPENSES = $2,248,224 – ($23,539 + $42,001 + $35,000) + $15,000 = $2,162,684
Example. Similarly, if someone decides to calculate EBITDA using Operating Income Format of Income statement, he may do using the below formula –
EBITDA = NET INCOME + TAXES + DEPRECIATION & AMORTIZATION = $1,713,269 + $36,300 + $498,655 + $100,000 = $2,348,224
3. OTHER INCOME STATEMENT FORMAT
It is often noticed that although Single & Multi-step income statements are quite useful from investor’s point of view and are completely in line with the principles laid under US GAAP; they often lack insights required for controlling & managing day to day operations of the company. Therefore, organizations often do come up with their own versions of income statement to be used by their managers and are published only for internal purposes.
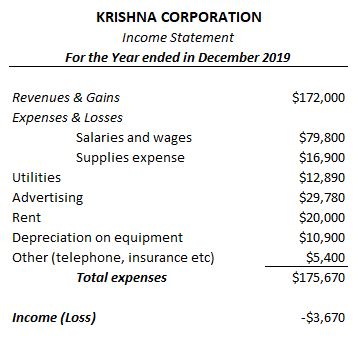
One such version called Contribution Margin basis format is captured and compared to the traditional income statement format below –
TRADITIONAL FORMAT : INCOME STATEMENT
CONTRIBUTION MARGIN FORMAT : INCOME STATEMENT
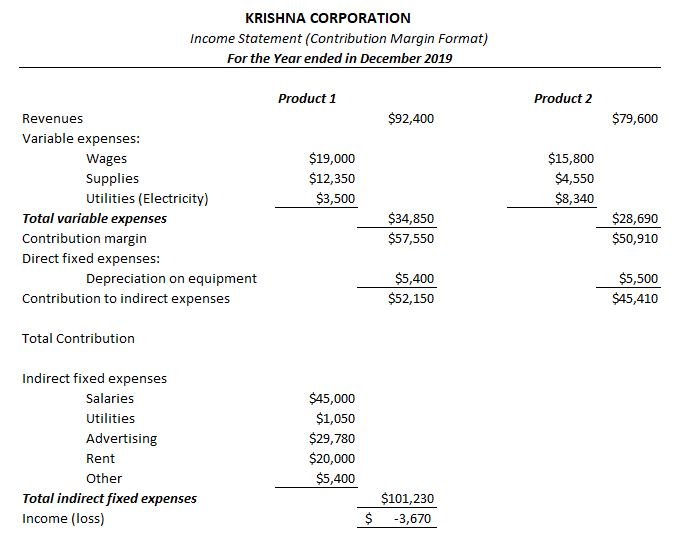
Contribution margin format of Income statement is more suited for managers to monitor and control costs related to each of their products or business functions. However; same format would become useless from investors or creditors point of view; who would be more interested in analyzing the financial health of the organization holistically.
It is important to note here that although companies are free to generate and publish contribution margin format; but it is to be used for internal purposes only and must not be circulated outside the organization for other stakeholders.