WORKING CAPITAL DEFINITION & EXAMPLE
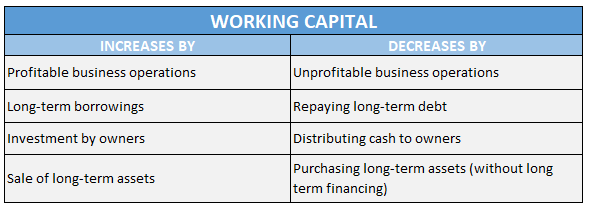
Working capital is a good indicator of the company’s short term financial health. It gives a fair idea of company’s liquidity & operational efficiency. Some texts also refer it as Net Working Capital. It can be calculated as below:
Components of working capital i.e. current assets and current liabilities can be understood as below:
- Current Assets are those resources of the company which can be converted into cash within a year or within the operating cycle of the company. Examples of current assets are cash & equivalents, inventory, accounts receivable, prepaid expenses, marketable securities etc.
- Current Liabilities are the obligations that a company owes and are to paid within a year or within the operating cycle of the company. Examples of current liabilities are accounts payable, short term loans, customer deposits, deferred revenue, accrued expenses etc.
A positive working capital implies that the company has sufficient liquid assets remaining to pay off its short term liabilities and finance its growth internally. It’s a good sign for company’s overall financial health. On the other hand, a negative working capital means company is very likely to face liquidity crisis in the near future. This may additionally lead to more borrowing, defer payments to creditors and suppliers and result in an overall lower corporate rating for the company.
Example. Say a company hold current assets worth $200,000 and current liabilities worth $180,000. In this case, the company is said to operate with a working capital of $20,000. Similarly, a company that holds $100,000 worth of current assets and current liabilities both is said to have NO working capital.
Note. Working capital is an amount even though it is usually discussed as part of financial ratios.
SCENARIO WHEN NEGATIVE WORKING CAPITAL IS OKAY
Businesses having high inventory turnover ratio & minimal credit period can still do well with negative working capital. These companies need little working capital being kept on hand as they have the potential to generate cash very quickly in short duration. Grocery stores like Walmart and Fast food chains like McDonalds are the ideal examples of such businesses. For these companies, products that are bought from suppliers are sold immediately to customers even before the company has to pay vendor or supplier.
On the other hand, capital intensive companies that have low inventory turnover ratio and long payment periods might always require to hold adequate working capital because of their longer sales/ operating cycles.
Table of Contents : Accounting Principles
Accounting Principles & guidelines